Certain types of RRDtool based Data Sources can from time to time generate what are look like to the casual observer spikes. These spikes can make your Cacti Graphs unreadable.
Spike happen when you either have set no maximum value on your
Cacti Data Template by using a 'U' as the Maximum Value,
or when certain COUNTER based RRDfiles have their counter data
overflow, and start counting again from zero. When this happens
recent versions of RRDtool, like version 1.7, handle these
overflows quite well, but for some older RRDtool versions, these
changes can result in these spikes.
There are also cases where for some reason the Cacti system goes offline, and therefore your Cacti Graphs will develop what are referred to as gaps.
Cacti provides two gap filling options from the user interface. In the image below, you can see the default Settings for Cacti's Spike Killer GUI.
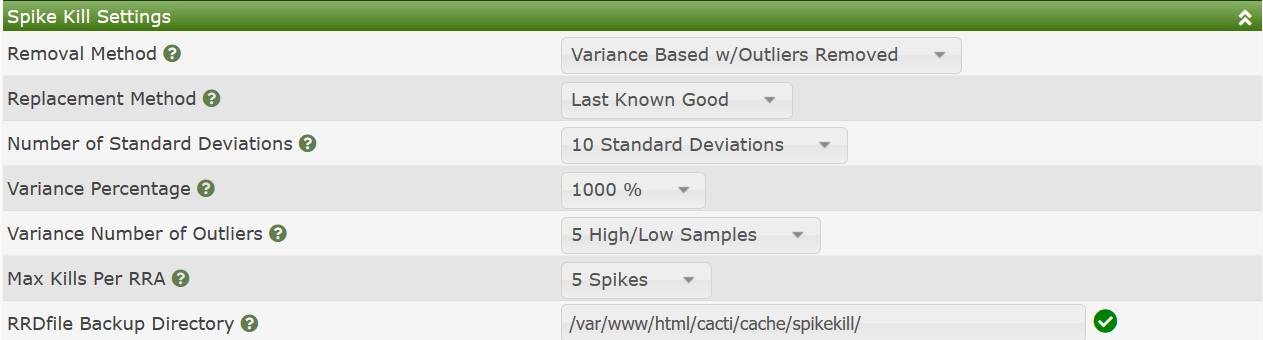
Those settings include:
Last Known Good, which would be
the last good known value, Average, which uses the Average
value for the RRDfile data source, and NaN's which will cause
the Graph to gap, but the spikes will be removed.Standard Deviations above the Average that are required
before the value is considered a spike. It only applies to
the Standard Deviation spike removal method.Variance spike
detection method, the percentage above variance before
considering a value a spike.Cacti also allows administrators to kill Cacti spikes on a periodic basis using a batch process. From this batch process, you select the time of day, the Graph Templates to perform Spike Kill operations on, and the backup retention for RRDfiles that have spikes removed from them. The image below shows those settings.
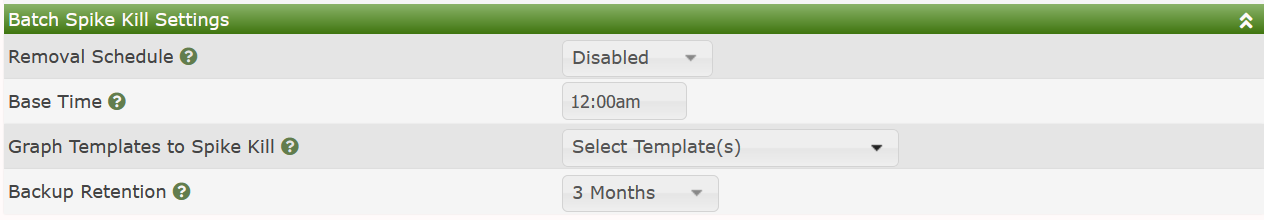
Of note is that first of all, the only Graph Templates that are
shown are Graph Templates that include COUNTER type Data Sources.
It is also worth noting that only Data Query type Graph Templates
are supported as of the current Cacti version.